Essential Guide to Coyote Diet: Discover Smart Choices for Wildlife in 2025
Coyote Diet: Understanding Their Unique Feeding Habits and Preferences
Coyote Feeding Habits: An Overview
Coyotes are renowned for their **omnivorous nature**, which allows them to adapt to a wide range of **food sources**. This dietary flexibility helps them thrive in diverse environments, from **urban settings** to **wild landscapes**. Typically, a coyote’s meal may include both plant and animal matter, showcasing their ability to exploit available resources efficiently. Understanding coyote **feeding habits** offers insights into their ecological role, predator-prey dynamics, and interactions with humans.
Coyote Food Preferences and What They Eat
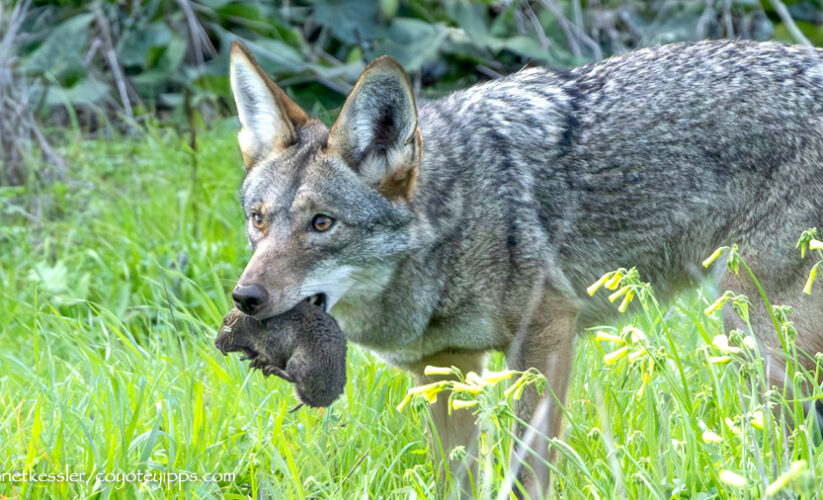
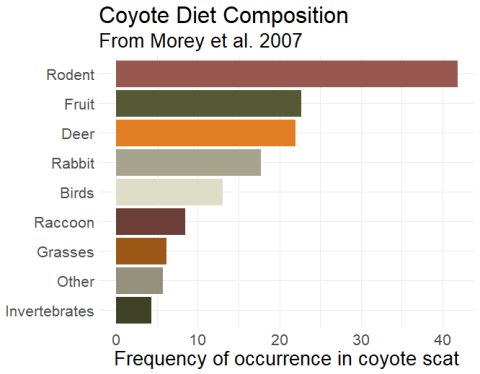
When exploring what do **coyotes eat**, it’s interesting to note that their **food preferences** can vary significantly based on their habitat and the time of year. In wilderness areas, coyotes often prey on small mammals like **rabbits** and **rodents**, which make up a significant portion of their diet. In **urban environments**, however, they may turn to small birds, fruits, and even scavenging for human food, which reflects their resourcefulness and ability to adapt their **dietary habits** to the surroundings. Analyzing coyote **food choices** also reveals crucial information about their role in maintaining ecological balance.
Coyote Diet Variations by Season
<pThe coyote's **seasonal diet** can fluctuate depending on the availability of certain prey or plant-based food. During the spring and summer months, the emergence of new hatchlings and seasonal fruits provides a rich array of **foraging opportunities**. Conversely, as winter approaches, coyotes tend to rely more on cached food or scavenging to meet their nutritional needs. This **seasonal adaptability** is a testament to their resilience and intelligence in the face of environmental changes.
Coyote Hunting Strategies and Prey Selection
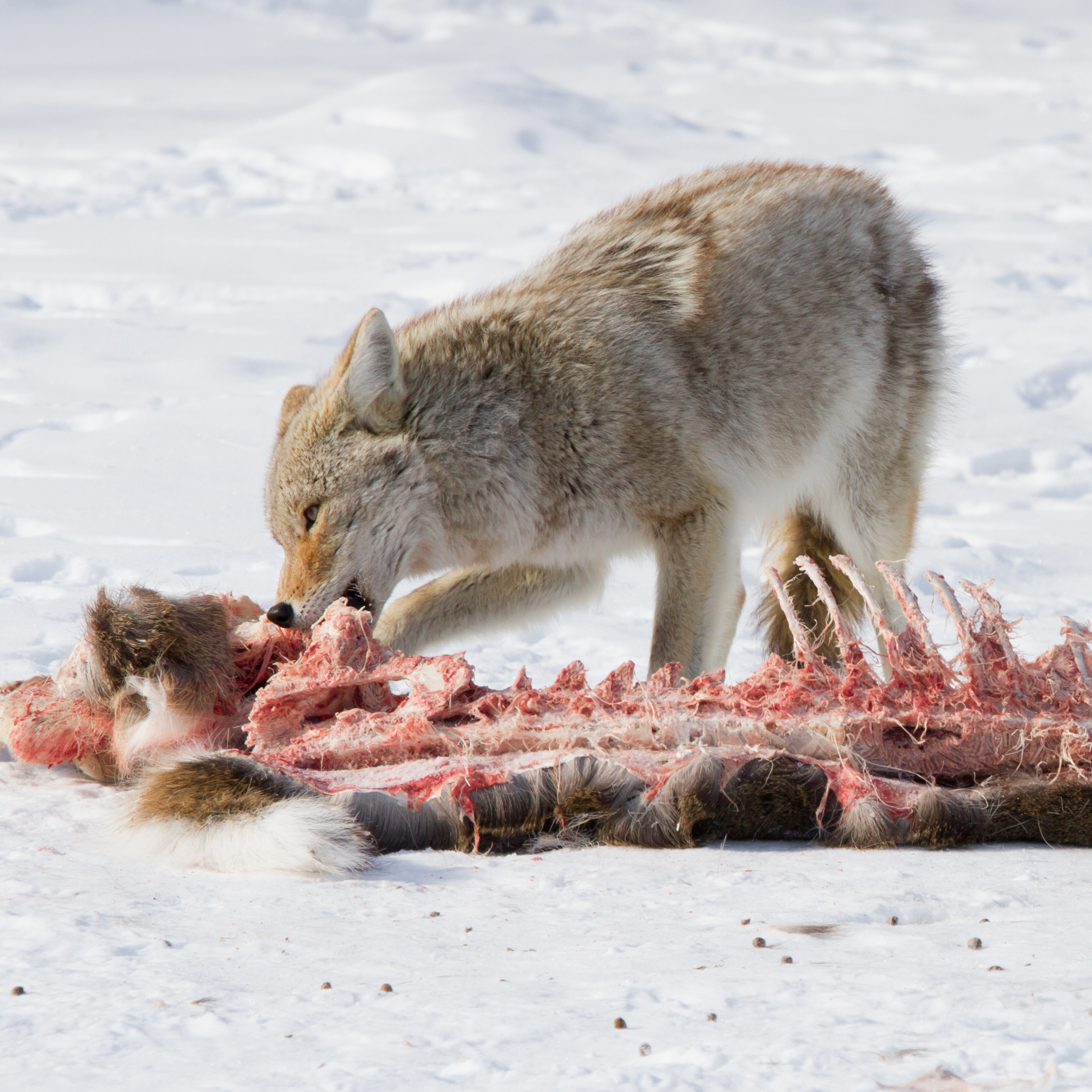
Coyote hunting is characterized by a blend of **stealth**, speed, and clever teamwork, particularly when hunting in packs. The choice of **coyote prey** varies significantly and is influenced by food availability and competition with other predators. Coyotes commonly engage in **communal hunting**, leveraging their social structure to bring down larger prey. Understanding these **hunting strategies** helps explain their significant role as predators within their ecosystems.
Coyote Hunting Techniques
Coyotes employ various **hunting methods**, leveraging their adaptability and intelligence to treat each hunting scenario uniquely. Common techniques include stalking prey quietly before pouncing or engaging in pack tactics to encircle and isolate a target. For example, a pack may use vocalizations to coordinate their movements, enhancing their chances of a successful haul. The **efficiency** of these strategies plays a critical role in their overall **survival strategies**, particularly in regions where food resources may fluctuate.
The Impact of Environmental Changes on Prey Selection
Environmental factors can significantly influence the prey available to coyotes. Changes in land use, depletion of habitats, and population dynamics of small mammals directly impact their **prey selection**. In urbanized areas, for instance, coyotes may pivot towards more accessible food sources like pets or garbage, ultimately leading to a reciprocal effect on local wildlife. Understanding these interrelations is vital to foster coexistence strategies and effective coyote management in human-affected areas.
Understanding Coyote Nutritional Needs
Coyotes have specific **nutritional needs** that vary based on their age, health, and environmental conditions. For example, young coyotes require more protein to support their rapid growth, while adults maintain their energy levels through a balanced intake of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Comprehensive knowledge of coyote **dietary habits** aids in understanding their influence on ecosystems and their competition dynamics with other wildlife.
The Role of Hunting Experience on Nutritional Intake
The effectiveness of a coyote’s hunting skills often personally relates to their **experience**. Factors such as age, previous hunting successes, and knowledge of local prey behavior contribute to their **nutritional success**. Coyotes that hunt in groups typically enjoy a more consistent food supply, impacting their body condition and **health**. Studying these variables can illuminate how behaviors evolve and shape the survival tactics of this adaptable predator.
Coyote Interaction with Livestock and Agriculture
Coyote interactions with livestock present a critical challenge for farmers and ranchers. While they can contribute to rodent control, they occasionally prey on domesticated animals, which expands their **relationship** dynamics with agricultural producers. Understanding these interactions is crucial in developing effective management strategies that protect both livestock and coyote populations, fostering coexistence while maintaining agricultural productivity.
Coyote’s Ecological Role and Impact on the Environment
Coyotes play a significant role in maintaining an ecological balance as both predators and scavengers. They help control populations of small mammals, like rodents, which can flourish without natural predators. This **ecological role** extends to their interactions with various species, including insects and carcasses, thus promoting **ecosystem diversity**. Moreover, their health and numbers can provide indicators of environmental integrity, showcasing the importance of biodiversity for a balanced habitat.
Coyote’s Impact on Local Wildlife Populations
The influence of coyotes extends to shaping local wildlife populations through predation and competition for resources. For instance, their presence can regulate small mammal numbers, contributing to an overall healthy ecosystem. Additionally, coyotes may affect the behavior of other large predators, introducing complex dynamics within the **food web**. Research on these interactions is essential to understand the environmental ramifications of coyote populations and address conservation measures that uphold ecosystem health.
Future Considerations: Coexisting with Coyotes
As human development encroaches on their habitats, future considerations for maintaining healthy coyote populations and protecting their ecological roles become increasingly important. Strategies such as public education about coexistence, management policies that account for their dietary and ecological needs, and conservation efforts that support natural habitats can benefit both coyotes and local wildlife. Engaging communities in **understanding coyote behavior**, ensuring the conservation of their habitats will be crucial.
Key Takeaways
- Coyotes are omnivorous and exhibit diverse feeding habits influenced by seasonal changes.
- Their hunting strategies are largely communal, relying on pack dynamics to effectively take down prey.
- Understanding their interactions with livestock and agriculture is vital for coexistence strategies.
- Coyotes maintain ecological balance by controlling small mammal populations, thus affecting general biodiversity.
- Future conservation efforts should focus on habitat protection and education to mitigate human-coyote conflicts.
FAQ
1. What are the primary food sources for coyotes?
Coyotes primarily feed on small mammals like **rabbits**, rodents, and birds. Despite this, their **omnivorous nature** allows them to incorporate fruits, plants, and even carrion into their diet, especially in urban areas where these resources are more accessible.
2. How do seasonal changes affect coyote diets?
Seasonal shifts greatly influence **coyote dietary habits**. During spring and summer, higher availability of prey and plant matter supports a diverse diet, while winter may prompt them to rely more on stored food or scavenging. This variation ensures they meet their nutritional needs year-round.
3. What role do coyotes play in the ecosystem?
Coyotes serve as significant predators, helping to control populations of smaller mammals, thus promoting a balanced ecosystem. Their presence also interacts intricately with other wildlife, influencing behavior patterns and contributing to the overall health of their habitats.
4. How do coyotes adapt to urban environments for food?
In urban environments, coyotes have shown remarkable adaptability by changing their **food preferences** to include human-related food sources, such as garbage and pets. This flexibility demonstrates their resilience and ability to thrive even in heavily populated areas.
5. What are the implications of coyote interactions with livestock?
Coyote interactions with livestock can lead to conflicts, particularly when they prey on domesticated animals. Managing these interactions through education and implementing preventive measures is essential in maintaining harmony between ranchers and wildlife while considering coyote influence on local rodent populations.
6. How does the coyote’s diet change in relation to competition with other species?
Coyotes respond to competition with other predators by optimizing their **prey selection** and **foraging behavior**. They may settle for smaller or more abundant prey when faced with competition, showcasing their dietary flexibility and ability to adapt to fluctuating ecological conditions.