Effective Ways to Manage Hypoglycemia Diet for Improved Health in 2025
Effective Ways to Manage Hypoglycemia Diet for Improved Health in 2025
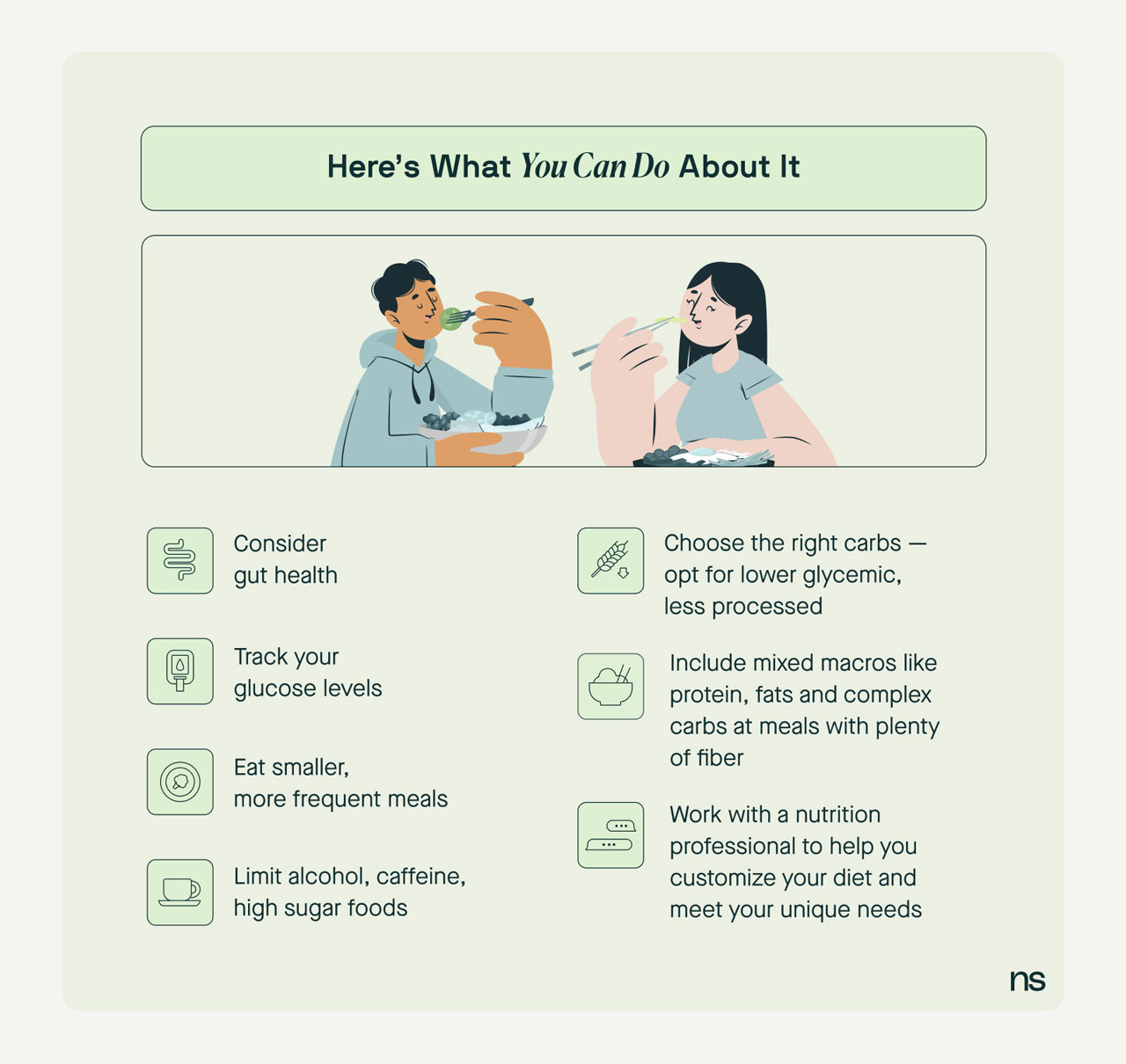
Understanding Hypoglycemia and Its Dietary Needs
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a condition that requires careful dietary management to maintain optimal glucose levels in the body. Understanding the intricate balance between **carbohydrate intake** and **meal timing** plays a crucial role in managing hypoglycemia effectively. The **hypoglycemia diet** is not just about avoiding sugar; it encompasses a holistic approach that favors **low glycemic foods**, **high fiber diets**, and mindful eating habits. These dietary strategies focus on preventing spikes and drops in blood sugar, which can lead to symptoms like fatigue, dizziness, and confusion.
The Importance of the Glycemic Index
One effective way to manage your hypoglycemia diet is by being educated about the glycemic index (GI) of various foods. The GI measures how quickly foods raise blood glucose levels. Foods with a low GI, such as whole grains and legumes, offer a slow release of energy, which helps to keep blood sugar stable. Conversely, high GI foods can cause quick spikes that lead to a crash later on. For example, pairing a **protein intake** source, like nuts or lean proteins, with complex carbohydrates can help in achieving a balanced glycemic response. Always consider **reading food labels** to make informed choices that support your **glucose management**.
Meal Planning for Effective Glucose Control
Meal planning is essential for successfully adhering to a hypoglycemia diet. Planning your meals around a balanced intake of carbs, proteins, and fats can help maintain steady blood sugar levels. Aim for three regular meals a day, supplemented by **healthy snacks** to avoid any drastic drops in glucose. Use **meal frequency** to spread your carbohydrate intake evenly throughout the day, ensuring that you’re balancing your **carbohydrates** effectively. **Hydration** also plays a vital role, so ensure consistent fluid intake, preferably through water or other non-sugary beverages, to maintain overall health.
Creating Balanced Meals
When organizing your plates, incorporate a variety of nutrient-dense foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Focus on **whole grains** for sustained energy, and be mindful of portion sizes to avoid overeating. For instance, a typical meal could consist of **lean proteins** such as chicken or fish, accompanied by a side of vegetables and a serving of brown rice or quinoa. Snack options like **nuts and seeds** or **fruit choices** such as berries can contribute to your overall dietary approach. The key to successful **meal preparation** is creating delicious, balanced meals that keep both your palate satisfied and glucose levels steady.
Healthy Snack Options for Managing Hypoglycemia
Healthy snacks play an integral role in managing **hypoglycemia** effectively between meals. Instead of reaching for high-sugar items that can cause sugar crashes, aim for **snacks for hypoglycemia** that combine protein, fat, and fiber. These snacks will help maintain energy levels and stabilize blood sugar. Incorporating a mix of whole foods, such as yogurt with berries or apple slices with almond butter, can keep you satiated without causing spikes in your blood sugar.
Snacking Strategies for Sustainably Energy Levels
When choosing snacks, it’s essential to look for options that contain **slow-releasing carbs** and healthy fats. Establishing a list of go-to snacks can make following your hypoglycemia diet easier. For example, crackers made from whole grains paired with hummus not only boost fiber intake but also provide essential nutrients without causing sudden blood sugar fluctuations. Avoid snacking on processed snacks high in sugar or refined carbohydrates, as these can quickly disrupt blood sugar levels.
The Role of Hydration in Managing Hypoglycemia
Staying properly hydrated is often overlooked in a hypoglycemia diet, yet it plays a crucial role in regulating **glucose levels**. Dehydration can alter the body’s response to insulin, making managing blood sugar more challenging. Aim to drink sufficient water throughout the day and limit dehydrating beverages like those high in caffeine or sugar. Fresh herbal teas and infused water can be delightful alternatives while still supporting **healthy eating habits**.
Meal Frequency and Its Impact on Blood Sugar Management
Establishing a routine that includes regular meal times can significantly aid in maintaining stable blood sugar levels. Skipping meals can lead to **sugar crashes**, and thus it is better to consume small meals throughout the day rather than infrequent large meals. Consider planning to eat every 3 to 4 hours, and if appetite allows, include nutrient-dense snacks between meals. This strategy ensures you’re maintaining an adequate energy balance, helping you avoid the symptoms associated with hypoglycemia.
Nutritional Guidelines for Successful Glycemic Control
When diving deeper into dietary recommendations, it’s vital to understand how different foods can either support or hinder blood sugar control. Educational resources, such as consulting with a dietitian, can provide personalized guidance tailored to your needs. A well-rounded **nutritional approach** will focus on incorporating complex carbohydrates, along with appropriate protein sources and healthy fats to create balanced meals tailored to your lifestyle.
Food Pairing for Better Blood Sugar Management
Effective blood sugar management often involves smart food pairings. For example, combining starchy foods with proteins can slow down sugar absorption and prevent spikes. Consider a meal with roasted sweet potatoes served alongside grilled chicken—this pairing not only boosts the meal’s nutritional profile but also assists in steady blood glucose levels. Make it a point to experiment with various flavor combinations for satisfying and **functional foods**.
Tracking Nutrients and Portion Control
In managing a hypoglycemic condition, understanding your body’s response to different foods is paramount. Keeping a **food diary** can help identify patterns and triggers that affect your blood sugar. Using **portion control** when consuming carbohydrates can help with better management. Learning to estimate portion sizes or using measuring tools can help you gauge your dietary intake more accurately. This structured approach will build a foundation for mindful eating and help you develop healthier eating habits for life.
Shop Smart for Heathy Choices
Smart grocery shopping is critical for success in managing hypoglycemia. When grocery shopping, aim to fill your cart with **nutrient-dense foods**, including plenty of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and lean proteins. Always look for **reading food labels** to understand the glycemic index and nutritional content of what you’re purchasing. Having a list before heading into your grocery visit can streamline the process and help you avoid impulse buys that don’t fit into your dietary guidelines.
Key Takeaways
- Implement a structured meal and snack timing to prevent blood sugar crashes.
- Utilize the glycemic index to choose low sugar foods that help sustain energy levels.
- Incorporate nutrient-dense foods like whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats.
- Continuously track your food choices and portions to develop substantial healthy eating habits.
- Stay well-hydrated to support overall health and mitigate glucose regulation issues.
FAQ
1. What are some recommended foods for hypoglycemia?
When managing hypoglycemia, prioritize **complex carbohydrates** like brown rice, quinoa, and whole grain bread. Incorporate **lean proteins**, such as chicken or legumes, and include **healthy fats** from avocados or nuts. Keep your meals balanced to promote stable glucose levels across the day, emphasizing **low glycemic foods** that release energy slowly.
2. How can meal timing affect blood sugar levels?
Meal timing involves organizing when you eat, which influences your body’s insulin response and blood sugar levels. Regular meals every 3-4 hours, filled with **nutrient-dense foods**, help maintain steady blood sugar without sharp contractions. This pattern encourages energy maintenance while preventing hunger pangs or drastic glucose fluctuations.
3. Are there specific snacks recommended for hypoglycemia?
Yes, incorporating **protein-rich snacks** like yogurt, nuts, and cheese can stabilize blood sugar levels. Pair these with **complex carbohydrates**, such as whole-grain crackers or fruit slices, to create sustained energy sources that avoid spikes associated with high-sugar snacks.
4. How does hydration influence blood sugar management?
Proper hydration significantly affects blood sugar control. Dehydration may cause higher blood sugar levels due to increased insulin resistance. Drinking plenty of water and avoiding dehydrating drinks helps maintain equilibrium within the body, supporting effective glucose management and overall health.
5. What strategies can help me with meal planning for hypoglycemia?
Developing a meal plan should include nutrient-dense options rich in fiber and protein. Automate your choices by using a structured meal framework—such as planning main meals around proteins and vegetative options, while regularly including healthy snacks can enhance your **sugar management** strategy effectively.
6. How do I read food labels to better manage hypoglycemia?
Reading food labels involving the **glycemic index** and nutritional information is vital in recognizing the effects foods may have on your glucose levels. Look for total carbohydrate content, portion sizes, and fiber content ensuring that you’re making informed decisions that align with your hypoglycemia diet goals.
7. What role do lifestyle changes play in managing hypoglycemia?
Making thoughtful lifestyle changes contributes significantly to **disease management** and glucose stability. Implementing activities that enhance physical health—such as exercise, adequate sleep, and appropriate stress management techniques—can directly support your dietary efforts and aid in stabilizing blood sugar levels.