
Effective Solutions for Gastroparesis Diet Modification in 2025: Improve Your Health Today
Effective Solutions for Gastroparesis Diet Modification in 2025: Improve Your Health Today
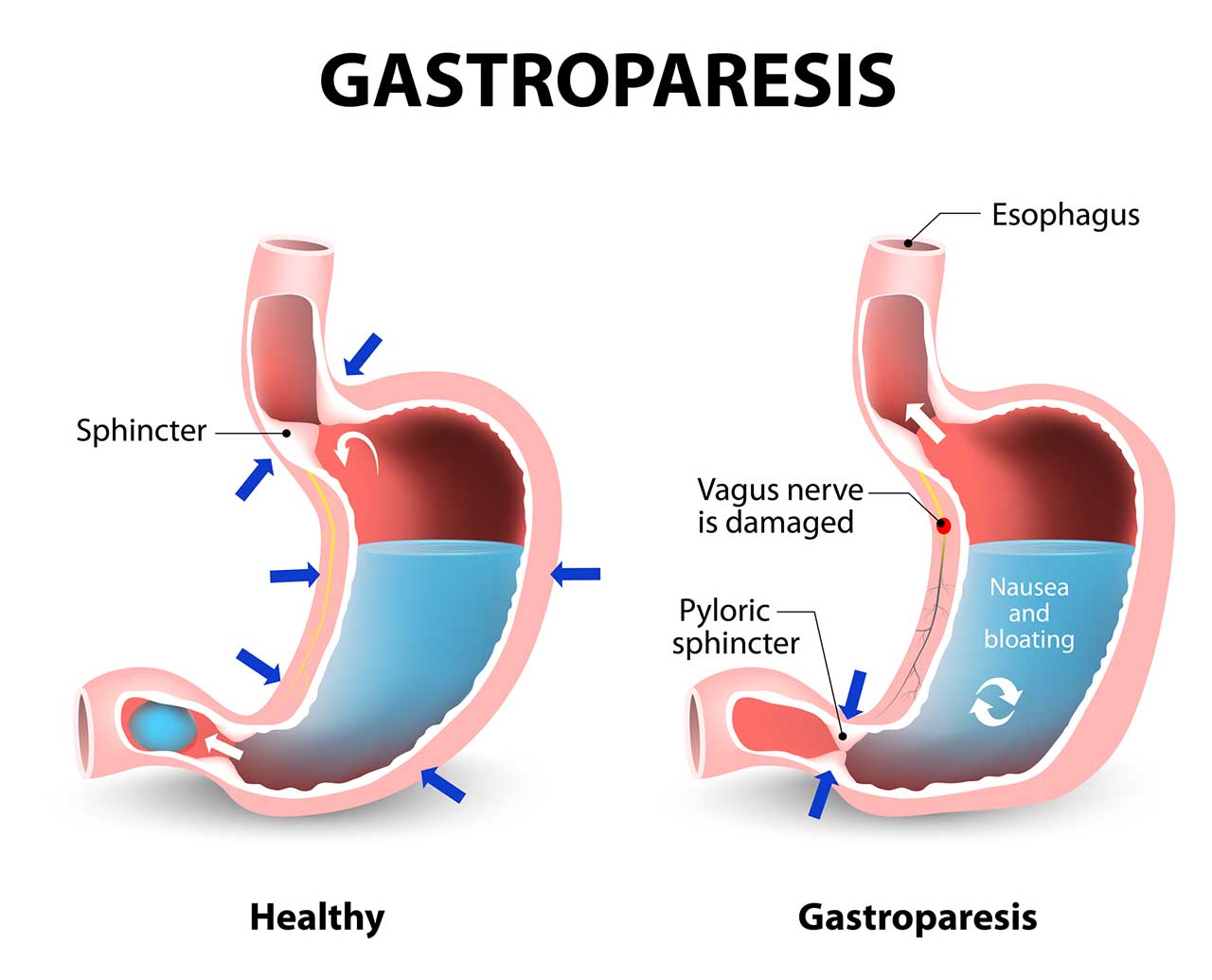
The **gastroparesis diet** is crucial for managing this complex and sometimes debilitating condition. This article explores the latest guidelines and strategies for modifying your diet in 2025 to effectively manage gastroparesis symptoms. By focusing on specific foods and meal planning strategies, you can significantly improve your digestive health and overall quality of life.
Understanding Gastroparesis Dietary Needs
Gastroparesis, characterized by delayed gastric emptying, requires careful dietary management. Understanding the reasons behind your dietary **restrictions for gastroparesis** is essential. The primary goal is to minimize symptoms such as nausea, bloating, and stomach discomfort. Often, a **low fiber diet** is recommended to ensure easier digestion. Fiber can slow down the digestive process, making it critical to limit high-fiber foods.
Foods to Eat with Gastroparesis
Choosing the right **foods to eat with gastroparesis** involves focusing on **easily digestible foods** that will be gentle on your stomach. Options include refined grains like white rice and pasta, lean proteins like chicken and fish, and low-fat dairy products such as yogurt. Incorporating nutritional elements like smoothies can help when you’re feeling too nauseous to eat solid food. These smoothies can combine easily digestible fruits, vegetables, and a good protein source, helping you maintain your nutrient intake without overwhelming your digestive system.
Foods to Avoid with Gastroparesis
When managing your **dietary restrictions for gastroparesis**, it’s equally important to know what to avoid. Stay clear of high-fat and greasy foods as they can exacerbate symptoms. Avoiding raw vegetables and **high-fiber foods** is also crucial because these can be more challenging to digest. Additionally, steer clear of carbonated beverages, as they may increase bloating and contribute to discomfort. By understanding and modifying your food choices wisely, you will have more control over your symptoms.
Meals Frequency and Timing
Implementing a strategy for **meal frequency** can significantly aid in managing gastroparesis. Eating smaller, more frequent meals reduces the burden on your digestive system and can mitigate feelings of nausea. Aim for 5-6 small meals a day instead of 2-3 larger ones. It’s also beneficial to maintain regular **meal timing for gastroparesis**, which helps regulate your digestive rhythms and promote better health outcomes.
Practical Tips for Modifying Your Diet
Dietary changes require commitment and strategic planning. Here are some practical tips on how to modify your diet effectively and maximize health benefits.
Meal Planning for Gastroparesis
Creating a **gastroparesis meal plan** tailored to your unique needs is an effective way to ensure you’re meeting your nutritional goals. Write down your weekly meals, focusing on **pureed foods**, protein sources, and low-fiber options. Incorporate cooking methods that retain nutrients while being easy on your digestive system, such as steaming or baking. Cooking from scratch lets you control ingredients while benefiting from the essential nutrients that support your health.
Incorporating Hydration
Staying hydrated is crucial when following a **low fat diet** for gastroparesis. Dehydration can exacerbate symptoms, so aim to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day. If plain water doesn’t appeal to you, try broth-based soups or **nutritious drinks for gastroparesis** like diluted fruit juices. Remember to spread your fluid intake throughout your meals for better digestion and symptom management.
Snacking Tips for Gastroparesis
Healthy snacking is key for managing hunger in between meals. Choose **safe snacks for gastroparesis**, such as low-fat yogurt, nut butters on low-fiber crackers, or smoothies with protein powder. These options not only provide necessary nutrients but also fit seamlessly into the small frequent meals you’re implementing. Track how these snacks make you feel to determine your preferences best.
Managing Symptoms with Diet
Effective management of gastroparesis symptoms through diet is essential for improving your quality of life.
Tracking Food Intake
Using a **symptom diary for gastroparesis** can help you understand how different foods impact your symptoms. By keeping a detailed record of what you eat and any reactions you experience, identifying triggers and patterns becomes easier. Consider incorporating your daily emotional and physical experiences into this log, as stress and emotional health can significantly influence digestive well-being.
Emotional Support and Community Engagement
Coping with gastroparesis can be challenging, and emotional support is often overlooked. Engage with **gastroparesis support groups** or online communities dedicated to sharing experiences and advice for managing diet and symptoms. Many people find solace and motivation in connecting with others who face similar challenges. Sharing your journey of **navigating dietary changes for gastroparesis** can provide real inspiration and useful tips.
Healthcare Professional Advice for Gastroparesis
It’s beneficial to consult with a healthcare professional or a nutritionist who specializes in **nutrition for gastroparesis**. They can offer tailored nutritional guidance and recommend any necessary **vitamin supplementation for gastroparesis** to prevent deficiencies. Keep an open line of communication with them to enhance your understanding of how diet impacts your overall health.
Key Takeaways
- Implement a **low fiber diet** consisting of **easily digestible foods**.
- Focus on eating **small frequent meals** to alleviate symptoms.
- Stay hydrated and consider nutritious drinks to supplement your diet.
- Engage with support communities and keep a detailed symptom diary.
- Seek guidance from healthcare professionals to tailor your dietary approach.
FAQ
1. What are the best **foods to eat with gastroparesis**?
The best **foods to eat with gastroparesis** include low-fat proteins (like lean meats and dairy), refined grains (such as white rice and pasta), and smooth purees. Smoothies with easily digestible ingredients also serve as excellent options when solid foods seem challenging to consume.
2. What are suitable **snacking tips for gastroparesis**?
When snacking with gastroparesis, focus on **safe snacks** such as yogurt, low-fat cheese, or high-protein options like nut butters and smoothies. These snacks can satisfy between meal hunger and ensure you’re meeting your nutritional needs while maintaining easier digestion.
3. How can I manage **hydration with gastroparesis**?
Hydration is essential for managing gastroparesis. Alongside drinking water, consider consuming diluted juices or broth-based soups. Spreading your fluid intake throughout the day helps in ensuring you remain hydrated without overloading your digestive system during meals.
4. How can a **symptom diary for gastroparesis** help?
Maintaining a **symptom diary** allows you to track your food intake against any symptoms experienced. This helps identify specific food triggers, and monitor your overall nutrient intake, facilitating better management of your condition through **dietary changes for gastroparesis**.
5. What role does a nutritionist play in the **dietary management of gastroparesis**?
A nutritionist can provide personalized strategies for managing gastroparesis through diet. They can help design **customized eating plans** that address individual needs while navigating the dietary limitations associated with gastroparesis, offering support and expert advice to optimize digestion and nutrient absorption.
6. Are there **safe foods for gastroparesis** I should focus on?
Safe foods for gastroparesis include soft, low-fat proteins (such as fish and poultry), soft fruits (like bananas), and well-cooked vegetables. Emphasizing these foods can help you manage symptoms while ensuring nutritional adequacy.
7. What **cooking methods for gastroparesis** are recommended?
Recommended **cooking methods** for gastroparesis include steaming, baking, and slow cooking, which can enhance the digestibility of foods. Avoid frying or broiling as these methods can incorporate too much fat and make foods harder to digest.